Nanomedicine
A major research focus in the Cheng Research Group is to develop therapeutic nanomedicine. We are interested in several platforms and directions. Polymer-drug conjugate has been one of the major platforms for the design of drug delivery systems and the development of new therapeutics. We have worked on drug-initiated ring-opening polymerization for the synthesis of polylactide-drug conjugate and nanoconjugates. We have developed size well controlled silica-drug nanoconjugates and explored the size-distribution and size-efficacy correlation. We also developed the concept of chain-shattering polymeric therapeutics. We are interested in cancer targeting and has developed aptamer mediated cancer targeting. We will continue working in this area and aim to develop novel chemistry for making advanced materials and systems that allow efficiency delivery of therapeutics in vitro and in vivo.
Drug-polymer conjugate via controlled ring-opening polymerization
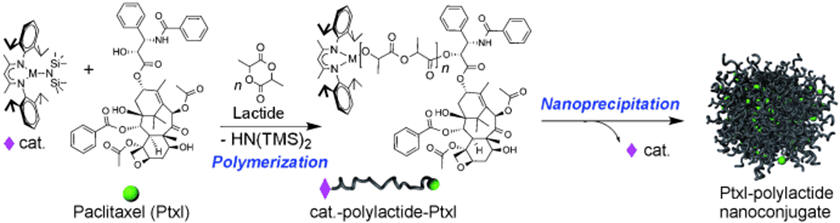
Tong et al. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47, 4830-4834. [PDF].
Tong et al. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2009, 131, 4744-4754 [PDF]
Tong et al..Bioconjugate Chem., 2010, 21, 111-121 [PDF].
Chan et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107, 2213-2218 [PDF].
Tong et al. Macromolecules, 2012, 45, 2225-2232. [PDF] [Link]
Tong et al. Chemical Science, 2012, 3, 2234-2239. [PDF] [Link]
Nanomedicine with controlled size for improved drug delivery and cancer targeting
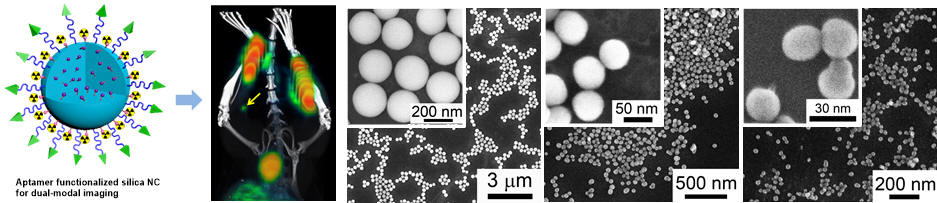
Tang et al. Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 124, 12893 -12898. [PDF] [Link]
Tang et al. ACS Nano., 2012, 6, 3954-3966 [PDF] [Link]
Cao et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 6494-6498 [PDF].
Cheng et al. Biomaterials, 2007, 28, 869-876. [PDF]
Farokhzad et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2006, 103, 6315-6320 [PDF]
Chain-shattering polymeric therapeutics
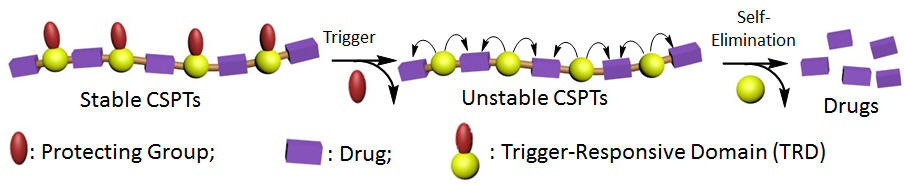
Zhang et al. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 2, 224-228. [PDF] [Link]
Zhang et al. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 6435-6439. [PDF] [Link]
Polypeptides: Synthesis, Structural Control and Applications
Polypeptide synthesis and application has been one of the major focuses in our group. In the past, we successfully developed organosilicon reagent mediated controlled ring-opening polymerization of amino acid N-carboxyanhydride. We also developed the first design of charged helical polypeptides, and this class of special polypeptides have been used in gene and siRNA delivery and cell membrane penetration. We will continue developing polypeptide biomaterials, aiming to design smart polypeptide materials, develop polypeptides that have therapeutic activity or efficient delivery functions, and improve the chemistry for the synthesis of polypeptides.
Polypeptide synthesis via ROP of NCA, helical charged polypeptide, gene/siRNA delivery
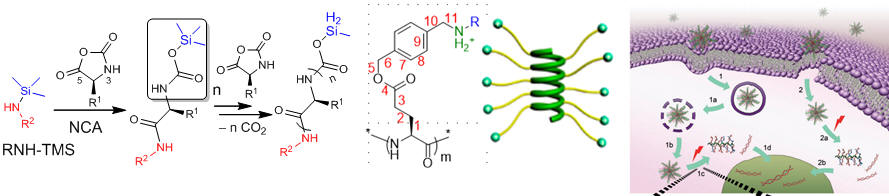
Lu et al. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2007, 129, 14114-14115.[PDF]
Lu et al Journal of American Chemical Society, 2008, 130, 12562-12563 [PDF]
Lu et al Journal of American Chemical Society, 2009, 131, 13582-13583 [PDF]
Wang et al. Journal of American Chemical Society, 2011, 133, 12906-12909. [PDF][Link]
Lu et al. Nature Communications, 2011, 2, 206. [PDF][Link]
Gabrielson et al. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51, 1143-1147. [PDF] [Link]
Yin et al. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25, 3063-3070. [PDF] [Link]
Yin et al Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5757-5761. [PDF] [Link]
Yin et al. Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 9182-9186. [PDF][Link]
Tang et al. Chemical Science, 2013, 4, 3839 – 3844. [PDF][Link]
Self-healing Materials Based on Hindered Urea Bonds
A new direction in the Cheng Research Group is to develop hindered urea bond containing materials. Hindered urea bonds can reversibly dissociate into isocyanante and amine, which form equilibrium with the urea bond via rapid exchange reactions. Based on this dynamic chemistry, we development polyurea and poly(urethane-urea) materials that display remarkable catalyst-free self-healing property at low temperature.
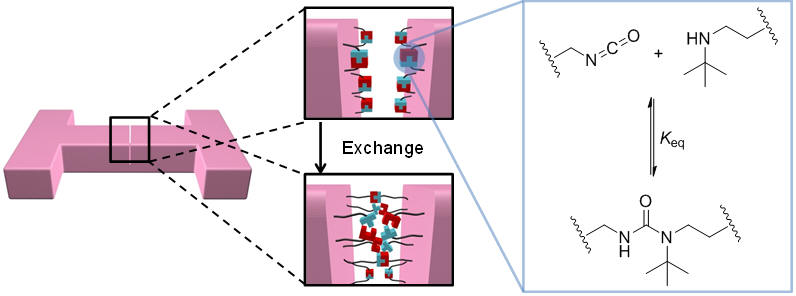
Ying et al., Nature Communications, 2014, 5, 3218. [PDF][Link]